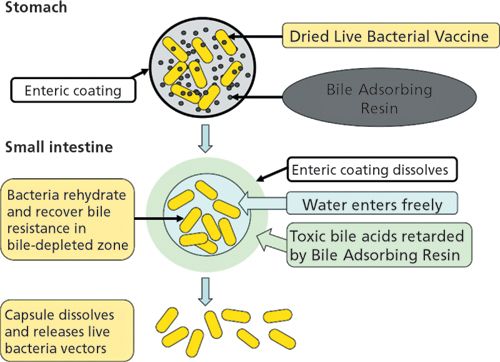
vaccine delivery system meaning
Vaccine-induced immune responses can be enhanced by mimicking the properties of pathogens. However many of the components used in vaccines occur naturally in the body in the environment and.
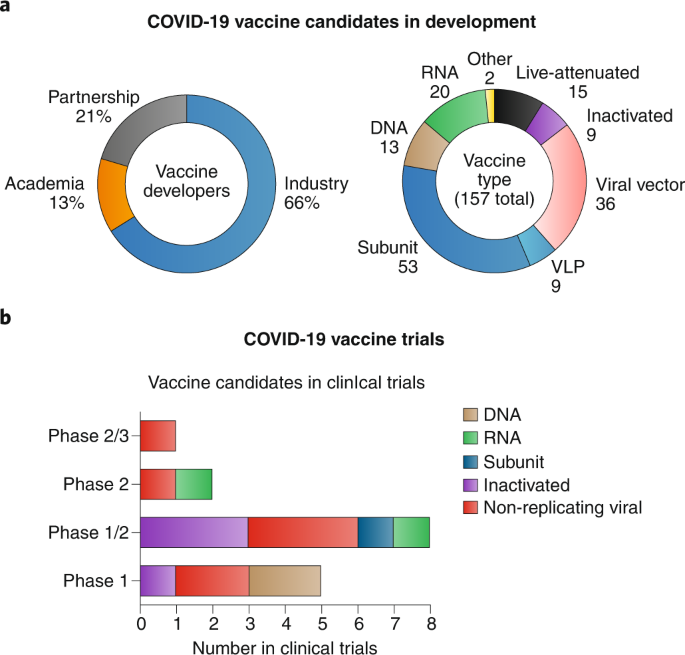
Covid 19 Vaccine Development And A Potential Nanomaterial Path Forward Nature Nanotechnology
A rational approach to the development of new and more effective vaccine adjuvants will require much further work to better define the mechanisms of action of existing adjuvants.

. Miniaturizing the vaccine delivery system also reduces the burden on the so-called cold chaina baton race from manufacturing plant to patient arm through a series of special. Most vaccine delivery systems are particulate including nanoparticles. 1 identifying an antigen and 2 developing a delivery approach for said antigen to achieve robust cellular and.
Pathogen-mimicking vaccine delivery system designed with a bioactive polymer inulin acetate for robust humoral and cellular immune responses - PMC Published in final. It travels by land and air and is stored in storage sites between delivery stages. Vaccine Delivery System Drug Repurposing and Application of Molecular Modeling Approach Drug Des Devel Ther.
The vaccine gets sent out from Pfizers US Germany and Belgium centers. In some studies delivery systems and immunostimulatory agents have been combined for more effective delivery of the immunostimulatory adjuvant into APC. The purpose of mRNA vaccines is to transfer RNA to cells for expression and subsequent production of protein antigens so as to induce an immune response against the.
The process of developing a vaccine consists of two key steps. Over the past decades the advent of recombinant cDNA technology has enabled the. Global equitable access to a COVID-19 vaccine particularly for health workers and other most-at-risk populations is the only way to mitigate the public health and economic.
Vaccine ingredients can look unfamiliar when they are listed on a label. Vaccines represent one of the most successful chapters in the history of medicine.
What Are Viral Vector Based Vaccines And How Could They Be Used Against Covid 19 Gavi The Vaccine Alliance

Non Viral Covid 19 Vaccine Delivery Systems Sciencedirect

Route Of Vaccine Administration Alters Antigen Trafficking But Not Innate Or Adaptive Immunity Sciencedirect

Covid Vaccines Save Lives But We Re Chasing A Moving Target Commonwealth Fund

Covid 19 Vaccine Deployment Risks Mckinsey

Covid 19 Vaccines For Homebound Patients And Their Caregivers Catalyst Non Issue Content
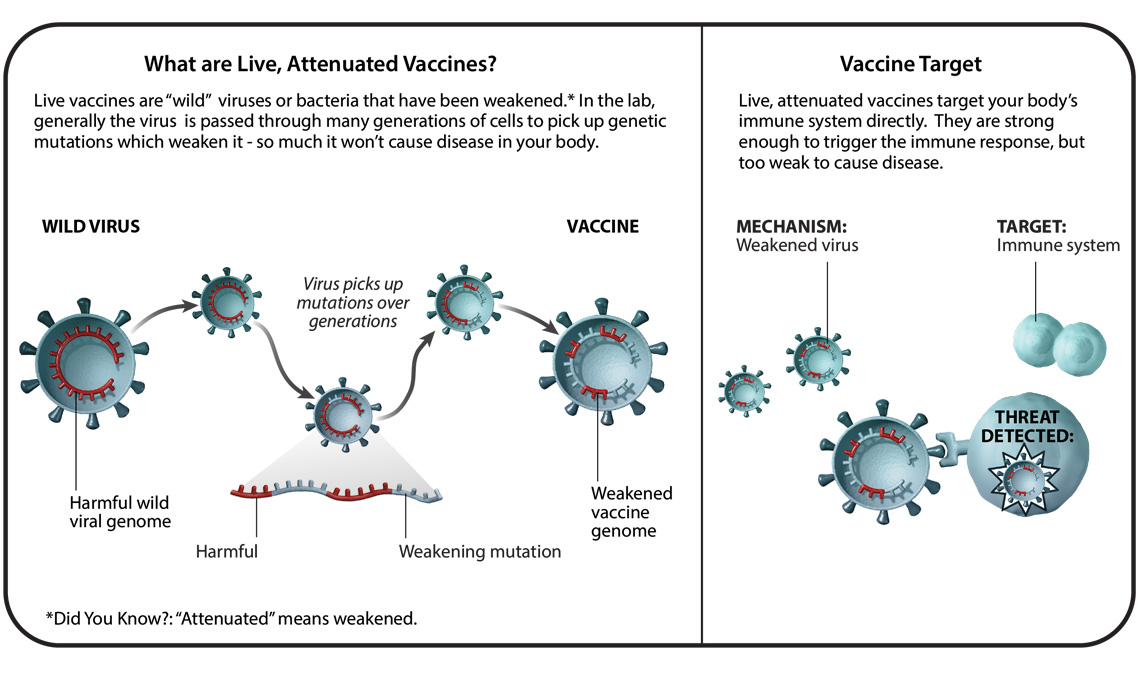
Understanding Six Types Of Vaccine Technologies Pfizer

Challenges In Ensuring Global Access To Covid 19 Vaccines Production Affordability Allocation And Deployment The Lancet

Recent Advances In The Discovery And Delivery Of Tlr7 8 Agonists As Vaccine Adjuvants Immunohorizons

Everything You Need To Know About The Vaccine Cold Chain Path

How The Sinovac Covid 19 Vaccine Works The New York Times

Vaccine Definition Types History Facts Britannica
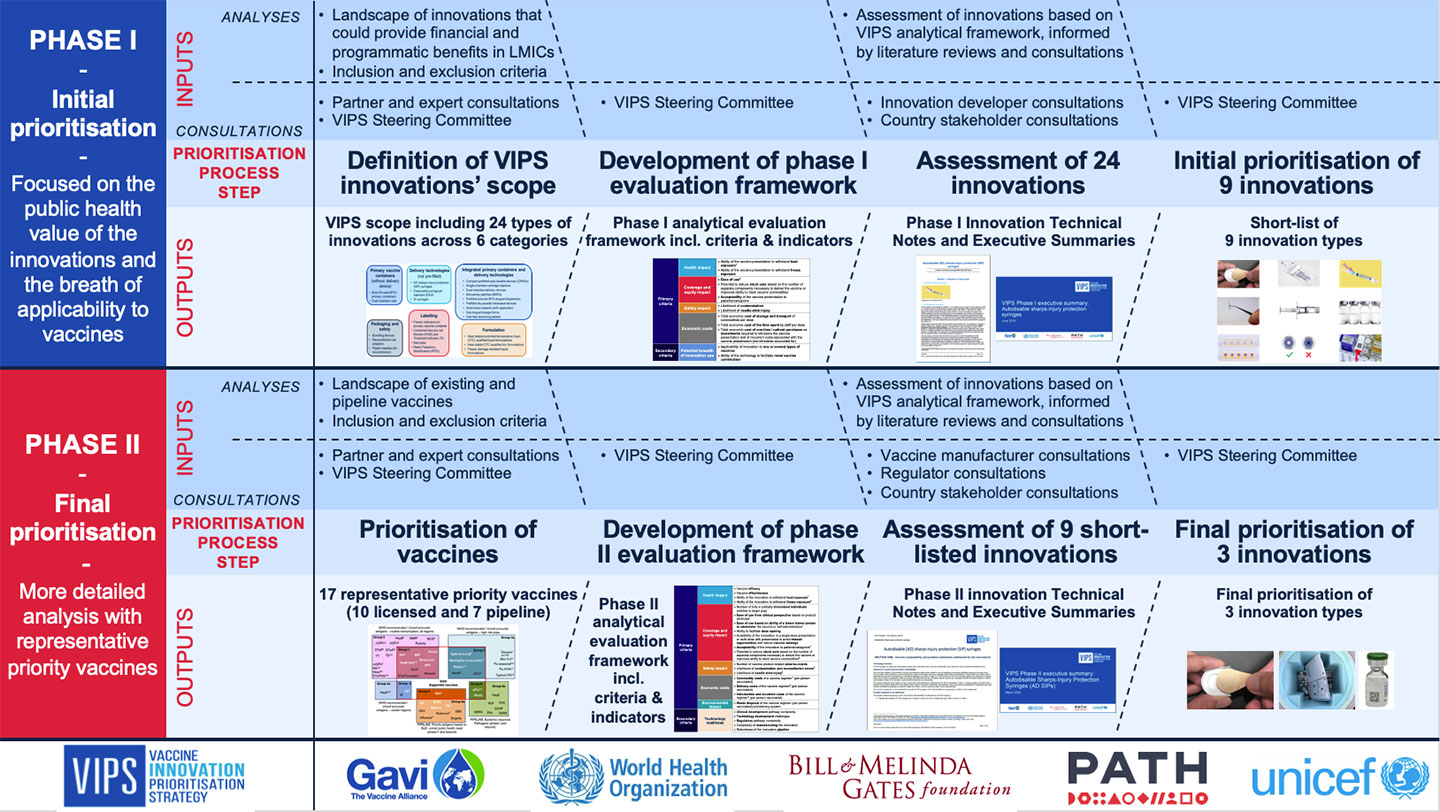
The Vaccine Innovation Prioritisation Strategy
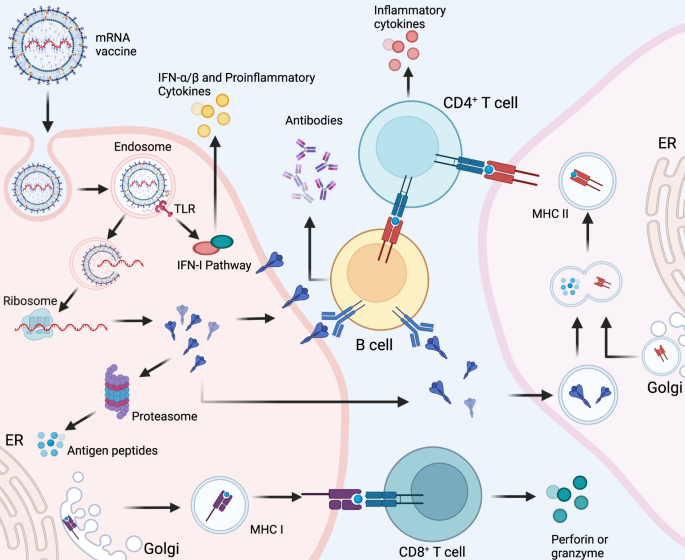
Advances In Covid 19 Mrna Vaccine Development Signal Transduction And Targeted Therapy

Nasal Spray Could Mean Needle Free Covid 19 Vaccine Nebraska Today University Of Nebraska Lincoln
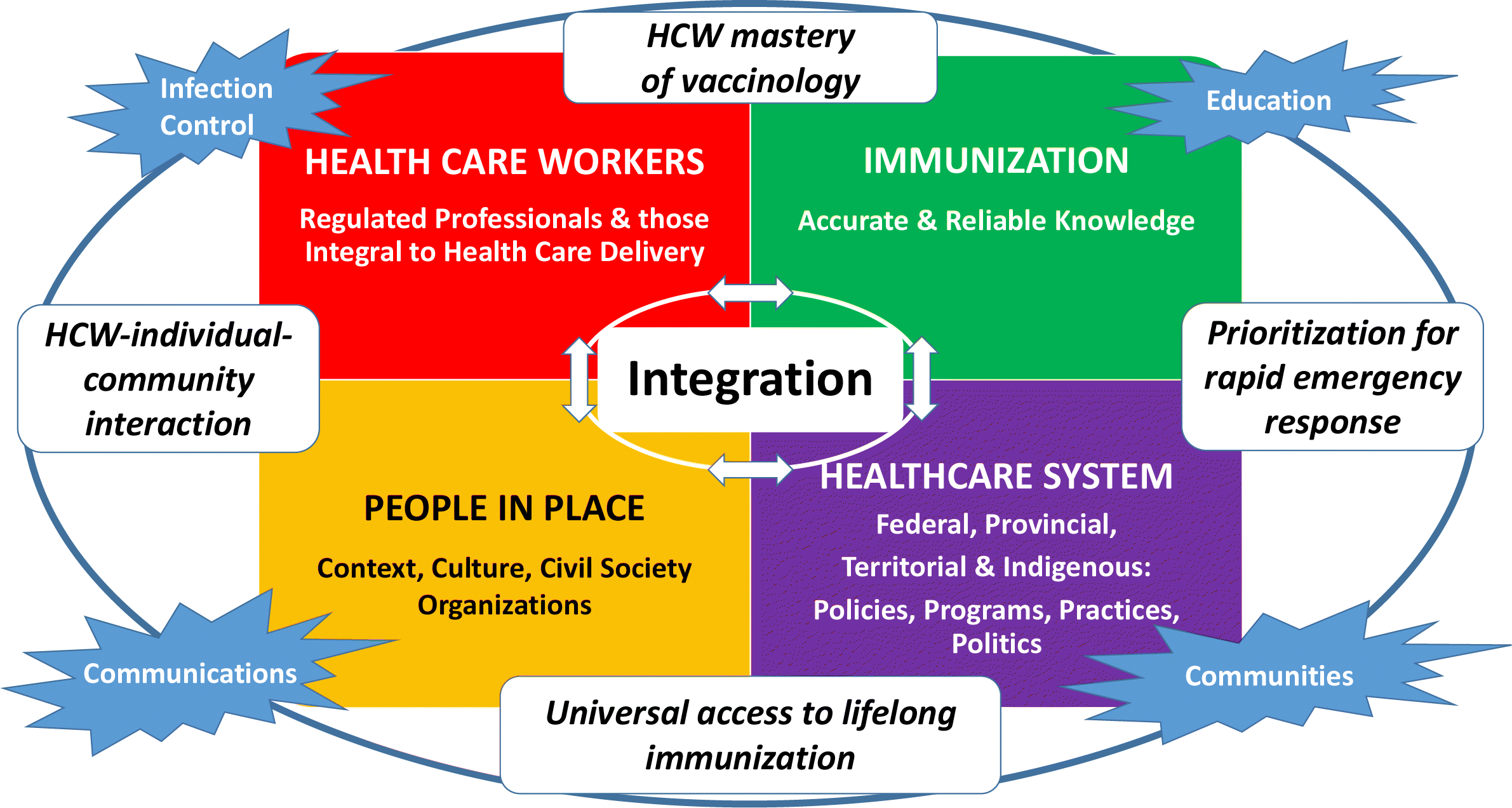
Royal Society Of Canada Covid 19 Report Enhancing Covid 19 Vaccine Acceptance In Canada
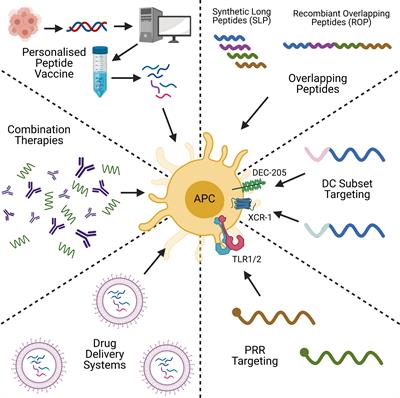
Frontiers Beyond Just Peptide Antigens The Complex World Of Peptide Based Cancer Vaccines

Neonatal Rotavirus Vaccine Rv3 Bb Immunogenicity And Safety In A Neonatal And Infant Administration Schedule In Malawi A Randomised Double Blind Four Arm Parallel Group Dose Ranging Study The Lancet Infectious Diseases